Typical Appearance In Vertical Cross Sections
-
Equivalent Potential Temperature and Relative Humidity:
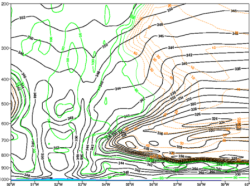
The equivalent potential temperature field shows the maximum temperature in the upper-level part of the eye . Air near the center of circulation (in the eye) is much warmer than that in the wider environment. In addition, a region with high mid-tropospheric relative humidity which supports good convection. It also moistens the atmosphere beyond the eyewall, helping to maintain the eyewall. -
Vertical Velocity (Omega):
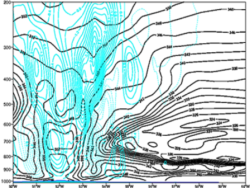
The vertical velocity shows varying winds as they move around the eyewall. -
Vorticity Advection:
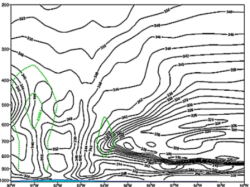
The vorticity advection shows cyclonic flow throughout most of the troposphere. Dashed lines are cyclonic (or counter-clockwise). Solid lines are anticyclonic (or clockwise). -
Fractional Cloud Cover:
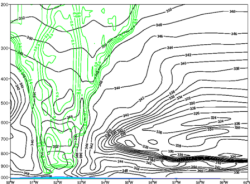
Fractional cold cloud cover shows the warm core from latent heat release
The vertical cross sections shown below were taken along 16°N, between 50°W and 60°W, for TC Bill (2009) on August 18th at 12:00 UTC:
|
18 August 2009 / 12 UTC. Pressure-longitude cross section at 16°N of potential temperature and relative humidity for TC Bill (2009). ECMWF (2-D) reanalysis data.
|
18 August 2009 / 12 UTC. Pressure-longitude cross section at 16°N of potential temperature and vertical velocity for TC Bill (2009). ECMWF (2-D) reanalysis data.
|
|
18 August 2009 / 12 UTC. Pressure-longitude cross section at 160N of equivalent potential temperature (K) and vorticity advection (s-1) for TC Bill. ECMWF (2-D) reanalysis data.
|
18 August 2009 / 12UTC. Pressure-longitude cross section at 16°N of equivalent potential temperature (K) and fractional cold cloud cover (0.50-1.0) for TC Bill . ECMWF (2-D) reanalysis data.
|