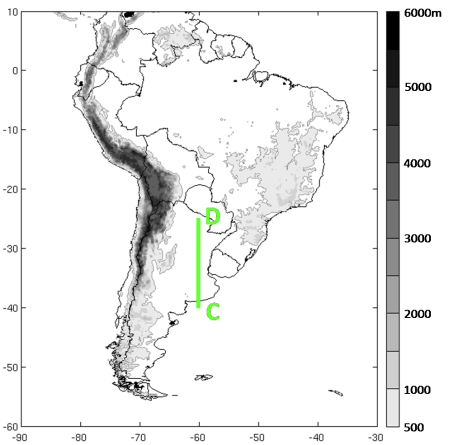
Typical Appearance In Vertical Cross Sections
Here are some relevant features from the NWP parameters that describe the vertical structure of the SALLJ events:
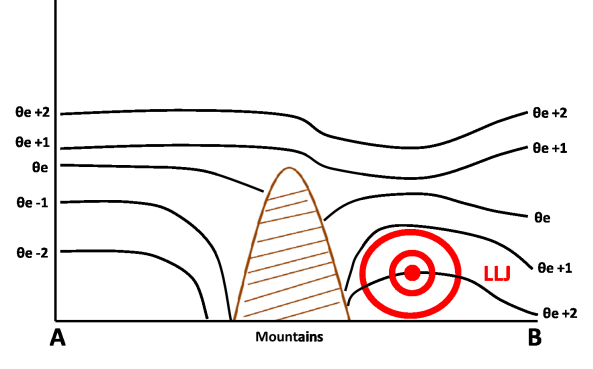
- Meridional wind: maximum of the northerly wind immediately to the east of the Andes at around 850 hPa.
- Equivalent potential temperature: statically unstable area accompanying the wind maximum.
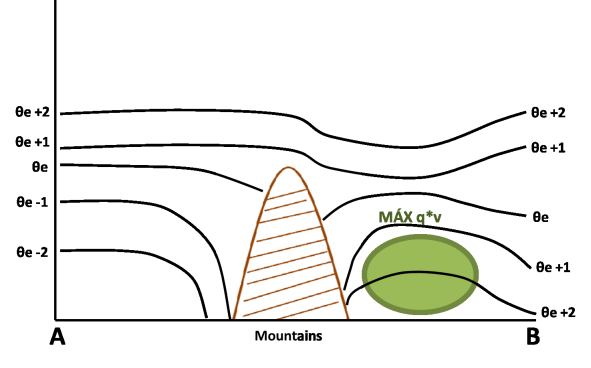
- Meridional moisture transport: maximum of moisture transport from tropical latitudes accompanying the wind maximum.
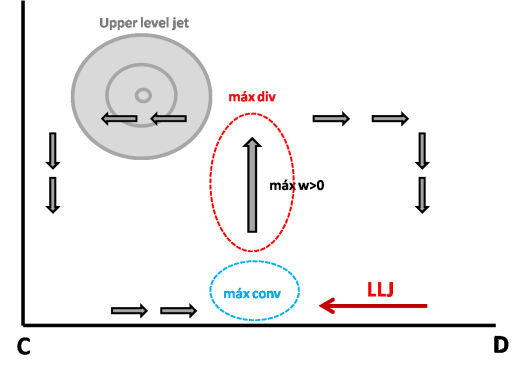
- Convergence and vertical motions: maximum of convergence at low levels and maximum of vertical motion at middle levels in the LLJ exit region.
Zonal vertical cross section
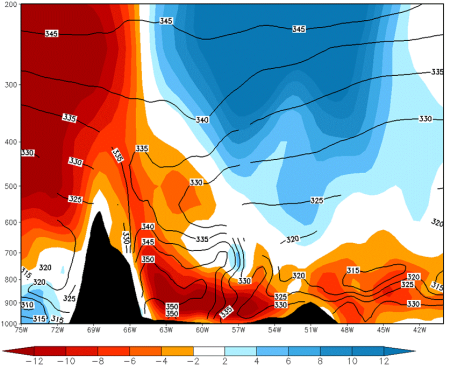
Meridional Wind and Theta-e
|
|
Lat: 27 °S. Meridional wind velocity (shaded, m/s); black: isentropes (theta-e, K) - 28 Dec 2002 12 UTC
|
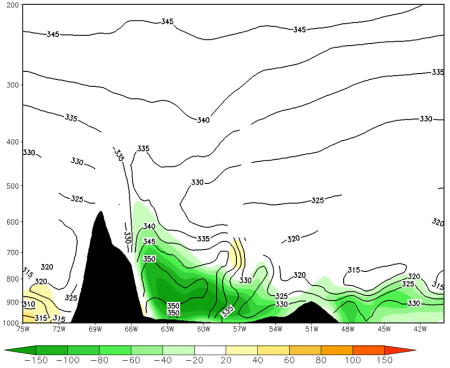
Meridional Moisture Transport
|
|
Lat: 27 °S. Meridional moisture transport (shaded, g/kg*m/s); black: isentropes (theta-e, K) - 28 Dec 2002 12 UTC
|
Meridional vertical cross section
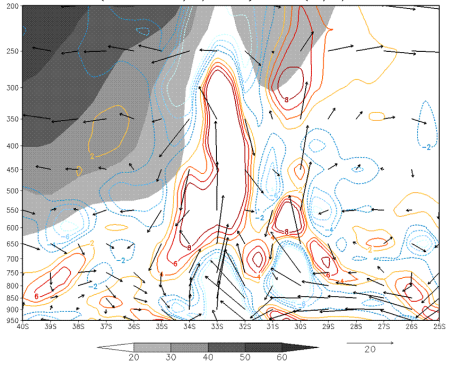
Low Level Convergence and Meridional Circulation
|
|
Lon: 60 °W. Zonal wind (shaded, m/s); contours: divergence; arrows: meridional circulation (m/s) 28 Dec 2002 12 UTC
|
.png)
k.png)