Typical Appearance In Vertical Cross Sections
- Isentropes:
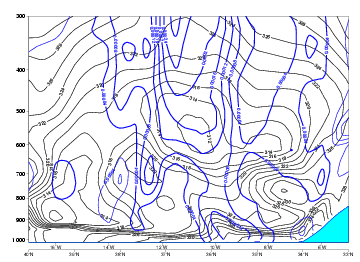
Often there is a conditionally unstable stratification in the lower and middle troposphere, with isentropic values decreasing with height. Otherwise isentropes show a shape of a ridge with the isolines far from each other in the area of the Upper Level Low. - Relative Vorticity:
Due to the cyclonic circulation within the Upper Level Low there is a maximum of relative vorticity. - Temperature Advection:
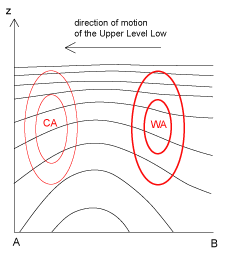
The air within an Upper Level Low is colder than in the surroundings. Therefore, there is distinct cold advection ahead of the Upper Level Low, and warm advection behind it. - Potential Vorticity:
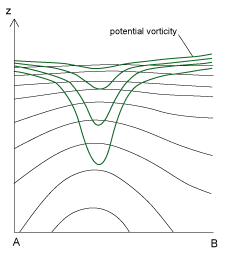
There is a maximum of potential vorticity above the centre of the Upper Level Low.
|
|
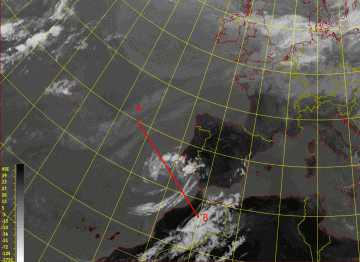
15 September 2005/12.00 UTC - Meteosat 8 IR 10.8 image; position of vertical cross section indicated
|
Relative vorticity
|
|
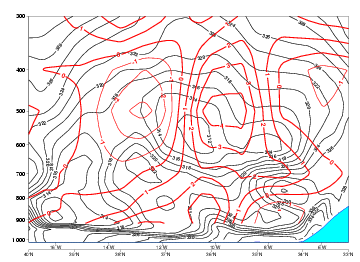
15 September 2005/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (Thetae), blue: relative vorticity
|
Temperature advection
|
|
15 September 2005/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (Thetae), red thin: temperature advection - CA, red thick:
temperature advection - WA
|
Potential vorticity
|
|
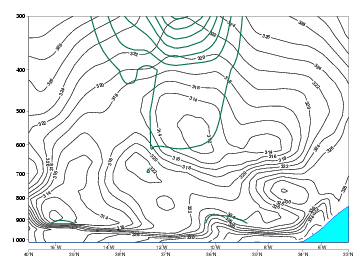
15 September 2005/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (Thetae), dark green: potential vorticity
|