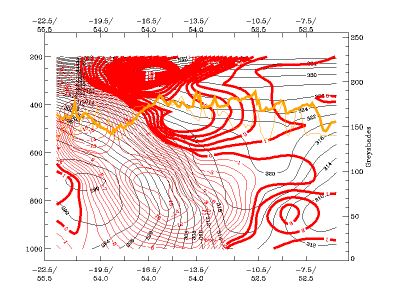
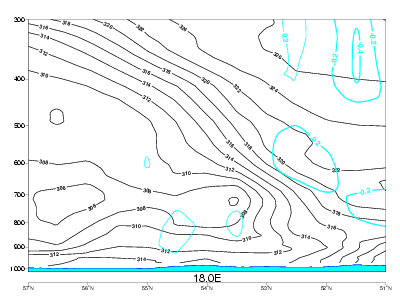
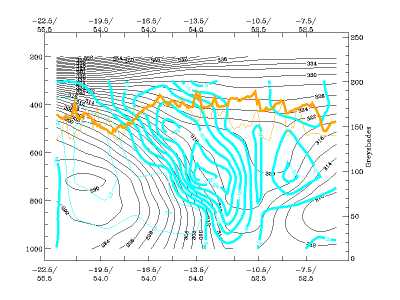
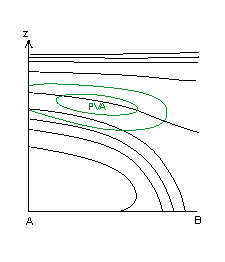
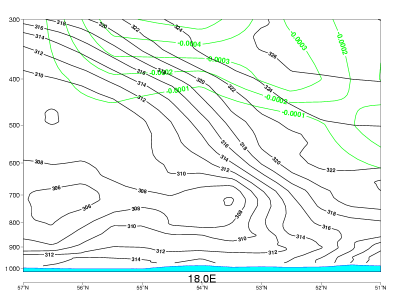
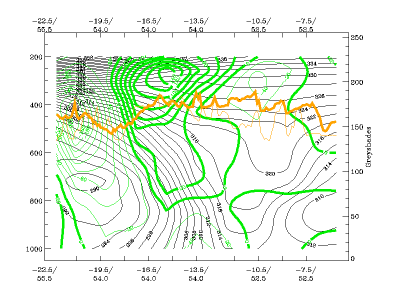
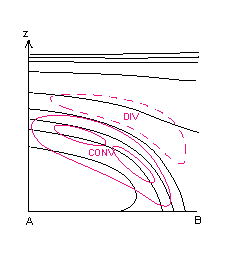
Typical Appearance In Vertical Cross Sections
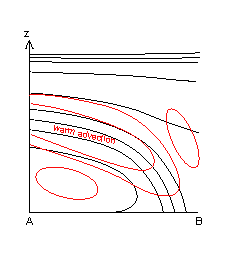
The vertical structure of CF in WA shows most clearly, that the front is indeed a Cold Front, despite being within warm advection.
Comparison of cross sections between a Cold Front and a Cold Front in Warm Advection (see Cold Front - Typical Appearance In Vertical Cross Sections ):
- TA: in CF warm advection ahead of the frontal zone and strong cold advection behind it, in CF in WA only weak warm advection is present
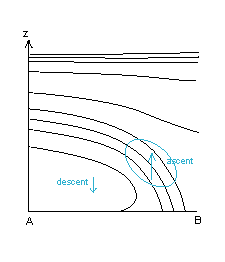
- Omega: in CF strong ascend ahead of the frontal zone and weak descend behind it, in CF in WA mostly only weak ascend on the middle levels
- PVA: In a CF the frontal zone is within PVA, which increases with height. The maximum is just below the tropopause. In a CF in WA there is only weak PVA on the upper levels.
- Divergence: convergence within the frontal zone, divergence above it. Features are similar in both types, but in CF they are stronger.
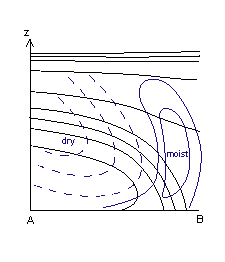
- Relative humidity: Humid air ahead of the frontal zone, dry air intruding into it from behind. In CF in WA the dry air does not penetrate through the whole frontal zone.
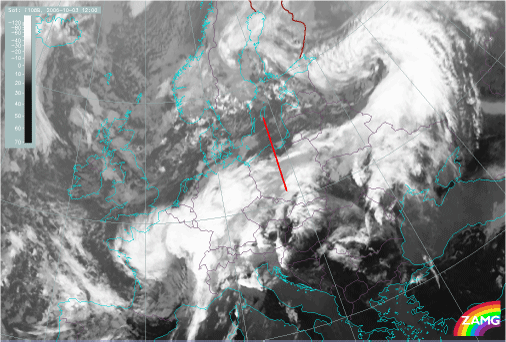
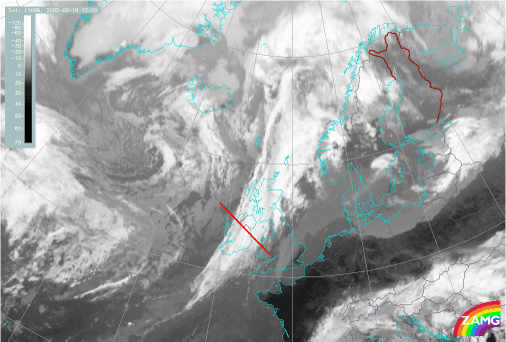
Locations of the cross section for both cases:
|
Cold Front in Warm Advection: 03 October 2006/12.00 UTC - Meteosat 8 10.8 image; position of vertical cross section indicated
|
Cold Front: 19 September 2005/12.00 UTC - Meteosat 8 10.8 image; position of vertical cross section indicated
|
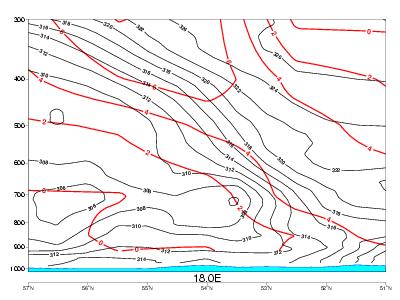
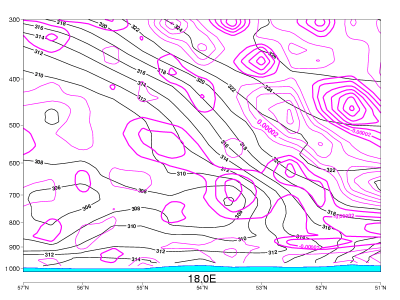
Temperature advection:
- In CF in WA the whole system is under weak warm advection.
- In CF there is warm advection above and ahead of the frontal zone and pronounced cold advection behind it, and partly within it.
|
03 October 2006/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes, red thick: warm advection, red thin: cold advection
|
|
|
19 September 2005/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes, red: warm advection (no cold advection present)
|
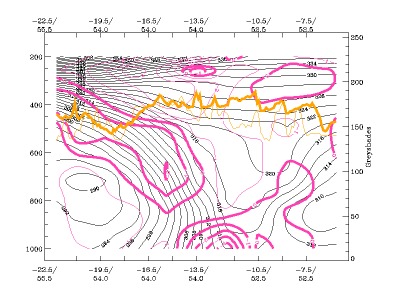
Vertical motion:
- In CF in WA there is weak ascent ahead of the frontal zone on the middle levels, and even weaker descent behind it.
- In CF there is strong ascent ahead of the frontal zone and descent behind it.
|
03 October 2006/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes, cyan thick: upward motion, cyan thin: downward motion
|
|
|
19 September 2005/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes, cyan thick: upward motion, cyan thin: downward motion
|
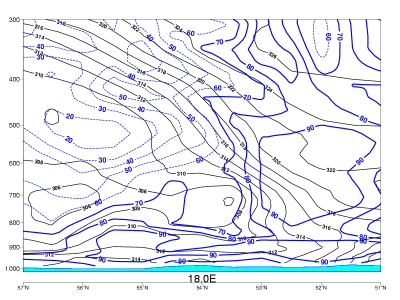
Vorticity advection:
- In CF in WA there is weak PVA on the upper levels.
- In CF the frontal zone is within positive vorticity advection, which increases with height. The maximum is just below the tropopause.
|
03 October 2006/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes, green: PVA
|
|
|
19 September 2005/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes, green thick: PVA, green thin: NVA
|
Divergence:
- In connection with fronts there is convergence within the frontal zone and divergence above it.
|
03 October 2006/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes, magenta thick: convergence, magenta thin: divergence
|
|
|
19 September 2005/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes, magenta thick: convergence, magenta thin: divergence
|
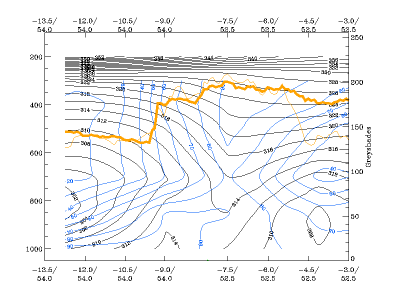
Relative humidity:
- The relative humidity is high ahead of the frontal zone and low behind it.
|
03 October 2006/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes, blue solid: relative humidity > 60%, blue dashed: relative humidity
< 70%
|
|
|
19 September 2005/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes, blue solid: relative humidity > 60%, blue dashed: relative humidity
< 70%
|