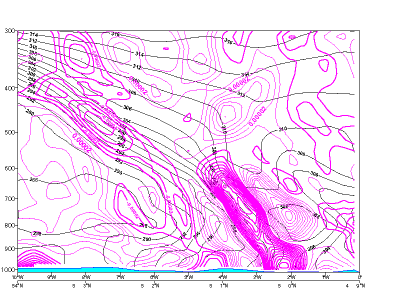
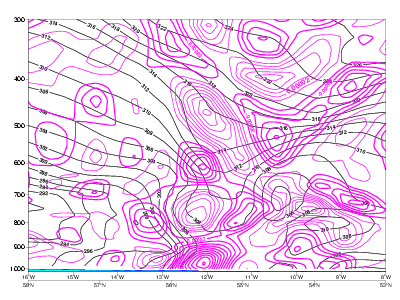
Typical Appearance In Vertical Cross Sections
Comparison of cross sections between a Cold Front and a Cold Front in Cold Advection (see Cold Front - Typical Appearance In Vertical Cross Sections):
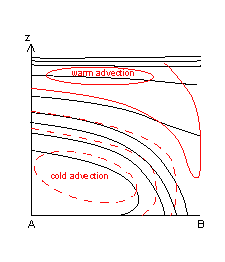
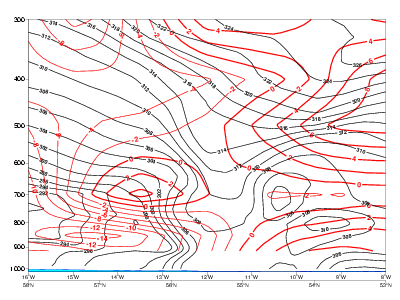
- Temperature Advection: in CF warm advection ahead of the frontal zone and strong cold advection behind it, in CF in CA cold advection within and behind the frontal zone, weak warm advection ahead of it.
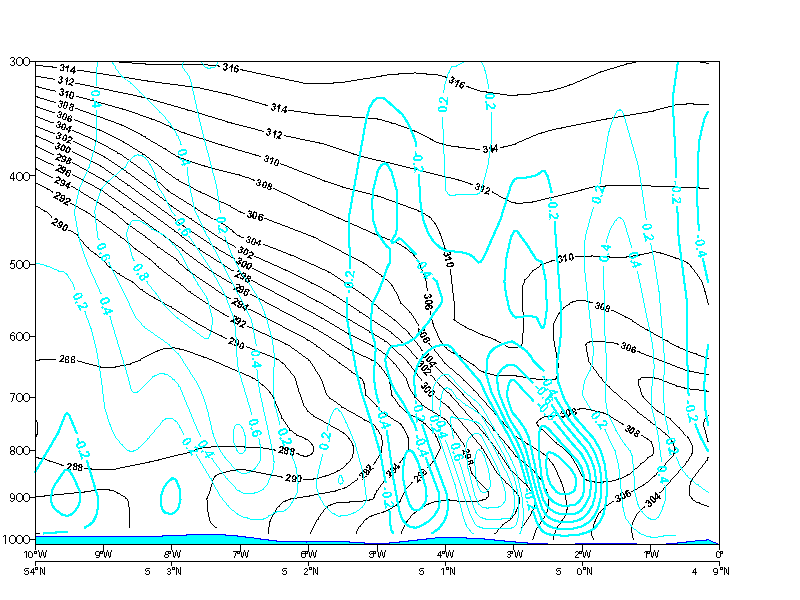
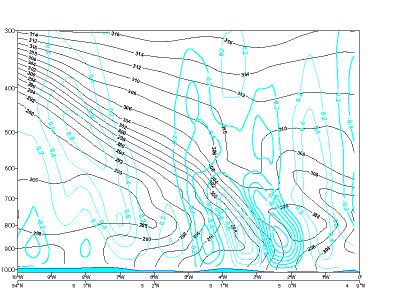
- Omega: strong ascend ahead of the frontal zone and weak descend behind it.
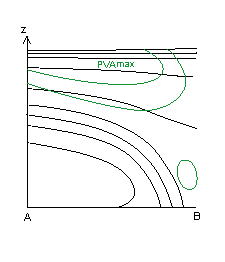
- Potential Vorticity Advection: the frontal zone is within PVA, which increases with height.
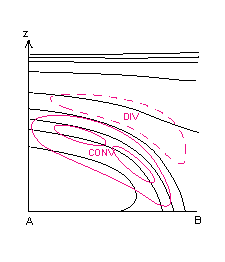
- Divergence: convergence within the frontal zone, divergence above it. Features are similar in both types.
- Relative humidity: Humid air ahead of the frontal zone, dry air intruding into it from behind.
|
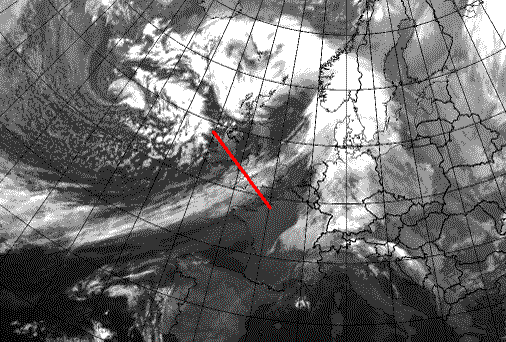
Cold Front in Cold Advection: 20 January 2007/06.00 UTC - Meteosat 8 10.8 image; position of vertical cross section indicated
|
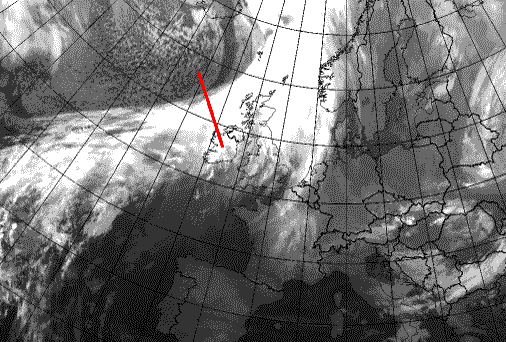
Cold Front: 10 November 2006/06.00 UTC - Meteosat 8 10.8 image; position of vertical cross section indicated
|
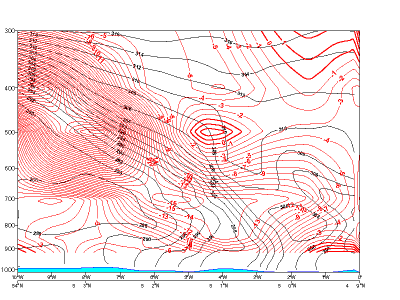
Temperature advection
|
20 January 2007/06.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes, red thick: warm advection, red thin: cold advection
|
|
|
10 November 2006/06.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes, red thick: warm advection, red thin: cold advection
|
Omega
|
20 January 2007/06.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes, cyan thick: upward motion, cyan thin: downward motion
|
|
|
10 November 2006/06.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes, cyan thick: upward motion, cyan thin: downward motion
|
Positive Vorticity Advection
|
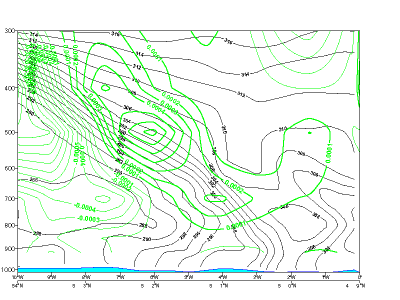
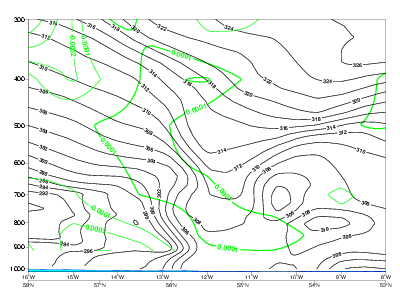
20 January 2007/06.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes, green: PVA
|
|
|
10 November 2006/06.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes, green: PVA
|
Divergence
|
20 January 2007/06.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes, red thick: warm advection, red thin: cold advection
|
|
|
10 November 2006/06.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes, red thick: warm advection, red thin: cold advection
|