Weather Events
The table below shows the main features of Zonda wind events. The differences in observed weather on the windward and lee sides of the Andes are emphasized.
| Parameter
|
Description
|
| Precipitation
|
- Precipitation produced by forced orographic ascent on the windward side.
- Heavy snowstorms may sometimes occur near the mountaintop, leading to road closures.
- No precipitation on the lee side.
|
| Humidity
|
- Extremely dry conditions on the Argentinian side.
- In the most severe cases, relative humidity may fall below 10% (very high dew point depression).
|
| Temperature
|
- Subsidence inversion on the Chilean side caused by a dry and stable subtropical anticyclone above a shallow maritime air mass.
- Cooling by orographic precipitation and ascent.
- Strong rise of temperature on the lee side.
|
| Wind (incl. gusts)
|
- Perpendicular to the mountain barrier, often with a northwesterly component.
- Strong and warm winds at the surface on the lee side of the mountains, with intermittent gusts.
|
| Cloud
|
- On the windward side stratocumulus, cumulus and altocumulus.
- Above the mountaintops "cap" or "barrage" clouds.
- On the lee side occasionally high cirrus, lenticular altocumulus clouds and rotor clouds.
|
| Other relevant information
|
- Dust storms are possible in dry regions near the Andes in Argentina, generated by strong winds at the surface.
- Visibility may fall considerably.
- The dry conditions and gusty winds favor the initiation and propagation of wildfires.
- Severe clear air turbulence possible, created by mountain waves.
|
|
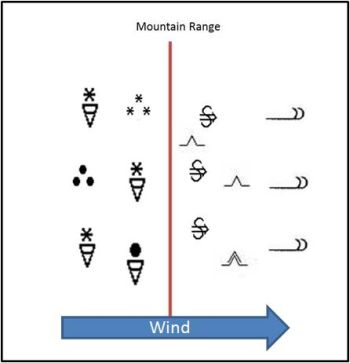
Schematic of synop observations and turbulence reports during Zonda events.
|
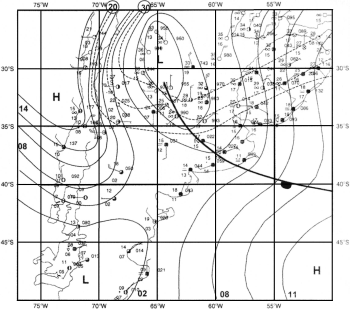
Surface analysis of 18 UTC 30 Aug 1999. Isobars (solid, hPa), isoterms (dashed, °C) and synop observations. From Seluchi (2003).
|
|
|
|
|
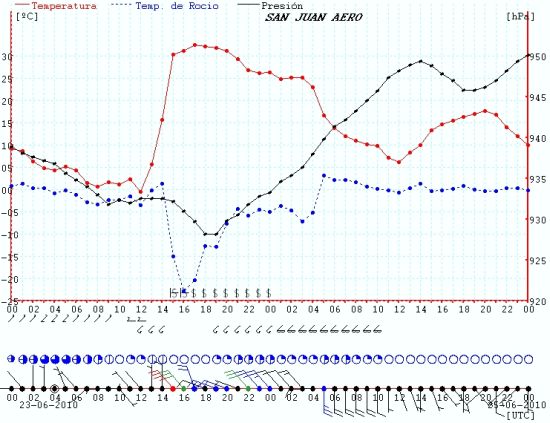
Time series of surface observations at San Juan airport during the 23-24 June 2010 Zonda event. Temperature (red), dewpoint (blue) and surface pressure (black). Temperature increase over 30°C and dewpoint decrease about 25°C in 3 hrs period. 35 kt winds and 53 kt gusts caused severe damage to buildings, widespread power outages and wildfires in the region.
|
|
|