Chapter V: Radar Images
Table of Contents
- Chapter V: Radar Images
- Radar Images
Radar Images
In this chapter, radar information from Asturias and Pais Vasco meteorological radars is presented. Both radars are situated close to the Spanish northern coast at elevations of 938 m for Asturias radar, and 632 m for Pais Vasco radar. Both radars were well located to catch the pressure system passage. These radars can work in short pulse mode (120 km Rmax, 900-1200 Hz PRF and 2×2 km horizontal Res.) or long pulse mode (240 km Rmax, 250 Hz PRF, and 1×1 km horizontal Res.)
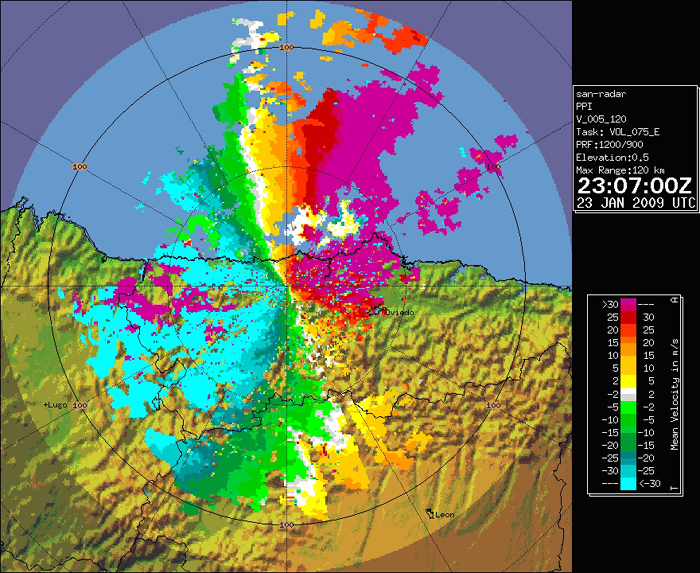
Below, short pulse Doppler mode images for Asturias radar at 23:07 UTC is presented. The displayed product in this case is radial wind velocity, in m/s. According to the attached scale, fuchsia pixels represent precipitation particles with radial velocities above 30 m/s away from the radar. The lightest blue pixels, represent, precipitation particles approaching the radar with radial velocities above 30 m/s.
Questions:
- Can you explain the presence of the fuchsia pixels areas west to the radar centre?
- Which velocity (approximate module and direction) could we assign to these pixels?
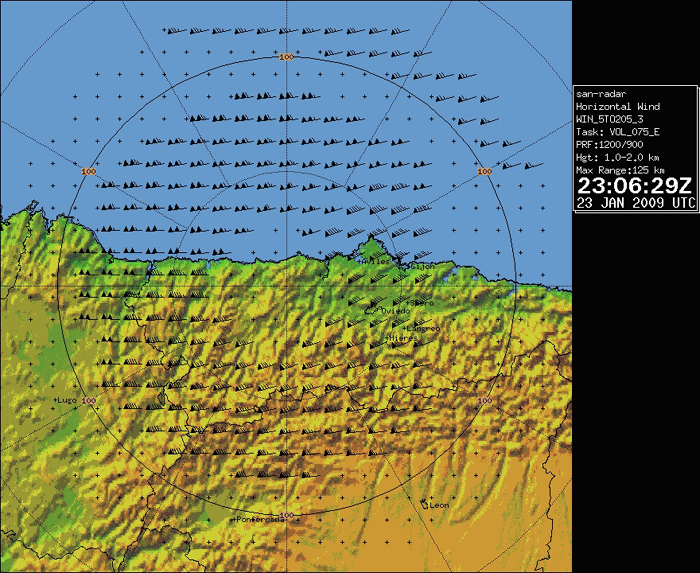
Also, a derived wind product is presented, for the same radar and time as the previous image. This product displays the areal mean wind taken at radar beam elevation. We have therefore to be careful not to assign these wind values to surface values. For that to be done, we would need to apply a correction based on soundings or vertical wind profiles.
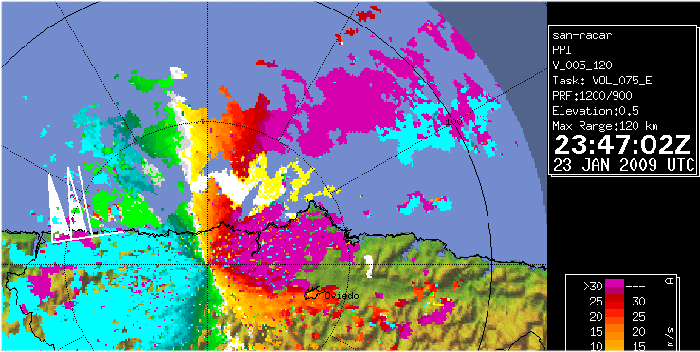
The maximum surface wind gust in the radar covered area, was registered at Cabo Busto automatic weather station, in Asturias region, with a value of 197 km/h. This weather station was damaged and out of work during some parts of the event, and got completely out of order after registering this maximum wind gust. For comparison with other wind observations at different places and levels, the before mentioned observation is plotted below, at the closest (in time) radial wind product. It has to be taken into account that the registered surface maximum wind, has not to be exactly correlated with the radial wind measured by the radar, which is taking its measures well above the surface. Also, orographic effects might have play a role that cannot be considered in this brief study.