Typical Appearance In Vertical Cross Sections
Jet Fibres usually develop in the vicinity of, or directly above a Warm or Cold Front, therefore it is not very easy to recognise them in cross sections. Moreover, the distribution of meteorological parameters reflects what is going on in those synoptic scale systems. In other words, Jet Fibres are not clearly seen in cross-sections and they have no specific appearance. However, the distribution of key parameters associated with the fibres can give some indicators for their most likely location.
Several vertical cross-sections, perpendicular to fibres, have been examined. Typical parameters studied were:
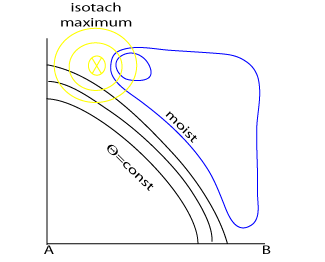
- Isotachs
The jet streak is located near the maximum radiance in WV and IR of the fibre
Fibres are located near to the jet axis, in most cases shifted slightly to the anticyclonic side - Relative humidity
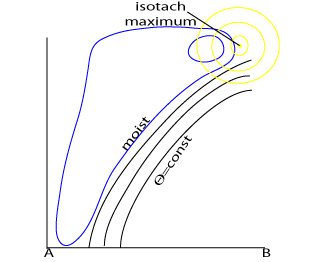
A fibre is sometimes located near a secondary humidity maximum, but the main humidity maximum represents the frontal cloudiness. - Isentropes
The slope of the isentropes shows the frontal zone
Jet Fibres behind the Cold Front
The isentropes show a downward inclined gradient zone of the Cold Front. The humidity distribution is dominated by the frontal humidity. High values of relative humidity can be found ahead of the frontal zone, along the slope of the isentropes. In some cases a secondary humidity maximum indicates a Fibre. The wind maximum is found right next to the Jet Fibre, with the Fibre being on the anticyclonic side of the jet.
|
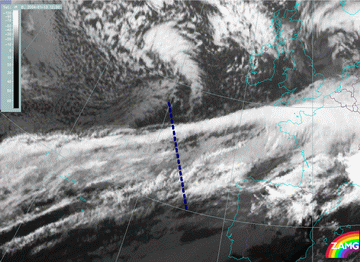
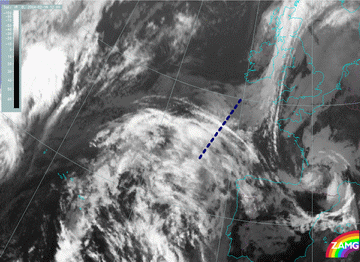
13 January 2004/12.00 UTC - Meteosat IR image; position of vertical cross section indicated from north to south
|
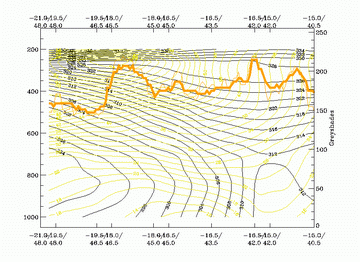
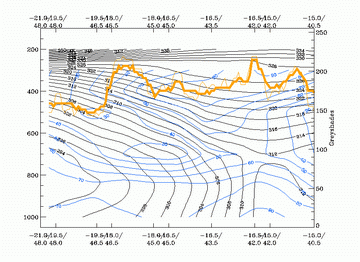
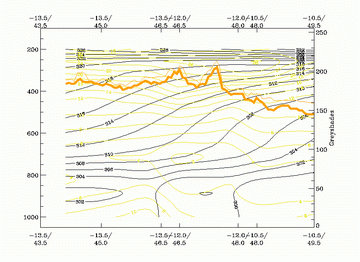
13 January 2004/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (ThetaE), yellow: isotachs, orange thin: IR pixel values,
orange thick: WV pixel values
|
|
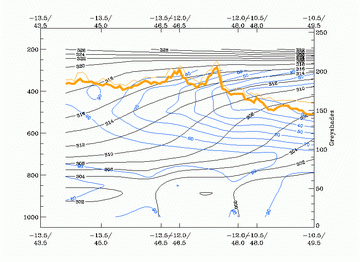
13 January 2004/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (ThetaE), blue: relative humidity, orange thin: IR pixel
values, orange thick: WV pixel values
|
|
Jet Fibres above the Warm Front Shield
The slope of the isentropes and the humidity distribution are typical for a Warm Front. The humidity maximum occurs along the slope of the isentropes. A secondary humidity maximum, representing the fibre, can be found on the anticyclonic side of the jet maximum. The jet maximum occurs above the forward part of the frontal surface.
|
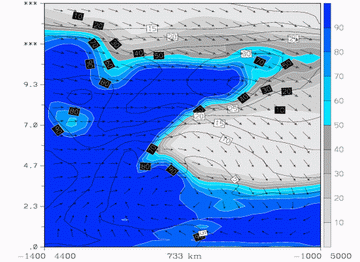
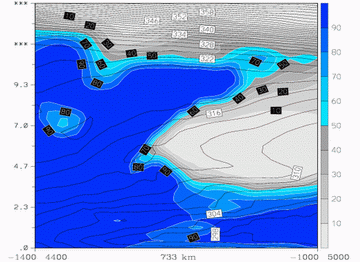
16 February 2004/12.00 UTC - Meteosat IR image; position of vertical cross section indicated from SW to NE
|
|
|
16 February 2004/12.00 UTC - ALADIN Vertical cross section; black: isotachs, blue: relative humidity, wind arrows superimposed
|
16 February 2004/12.00 UTC - ALADIN Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (ThetaE), blue: relative humidity
|
|
16 February 2004/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (ThetaE), yellow: isotachs, orange thin: IR pixel values,
orange thick: WV pixel values
|
16 February 2004/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (ThetaE), blue: relative humidity, orange thin: IR pixel
values, orange thick: WV pixel values
|
Distribution of wind, humidity and equipotential temperature in a cross section through a Warm Front.
If one compares Aladin and ECMWF cross-sections, it is clear that the ECMWF model does not resolve humidity in the upper troposphere well enough. The Aladin cross sections show a much better humidity distribution along the frontal zone and in the region where Jet Fibres occur.