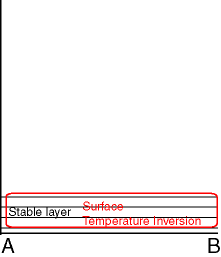
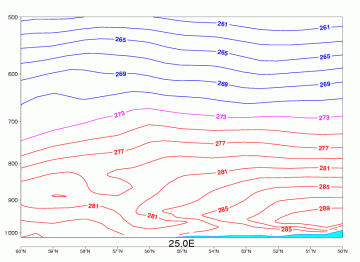
Typical Appearance In Vertical Cross Sections
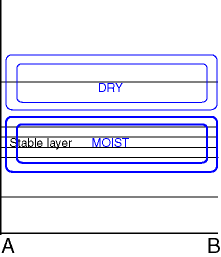
Fog and stratus are boundary layer phenomena, and vertical cross sections should preferable be zoomed into the lowest 300 or 500 hPa or the atmosphere to see the features most conveniently.
- Relative humidity:
A moist lower troposphere and relatively dry layers above typical for both radiation and advection St/Fog. - Total Cloud cover:
High (over 80%) cloud cover either very near or at the surface (both fog types ) or slightly lifted off the surface (advection St/Fog). - Isentropes:
Potentially stable situation at the lowest part of the troposphere. - Temperature:
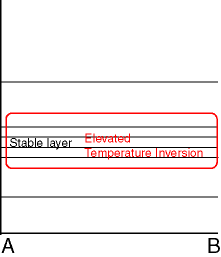
Surface (for both fog types) or elevated (for advection Stratus) temperature inversion.
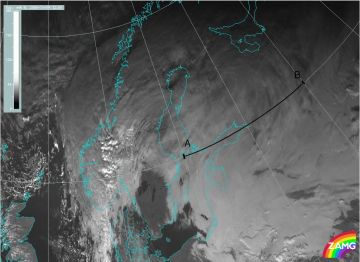
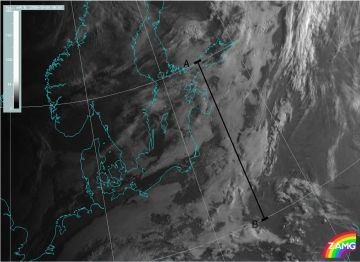
Advection Fog/St
|
|
09 November 2005/12.00 UTC - Meteosat 8 HRV image; position of the Vertical Cross Section indicated
|
Radiation Fog
|
|
04 October 2005/06.00 UTC - Meteosat 8 HRV image; position of the Vertical Cross Section indicated
|
Relative Humidity
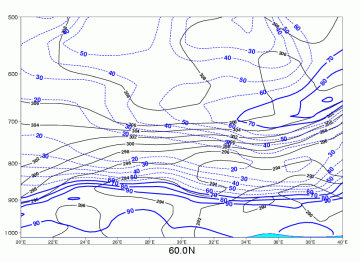
Advection Fog/St
|
|
09 November 2005/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; blue: relative humidity
|
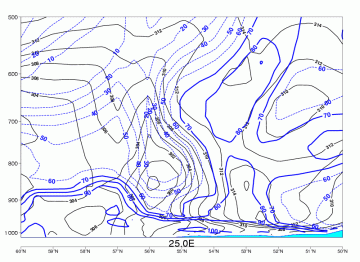
Radiation Fog
|
|
04 October 2005/06.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; blue: relative humidity
|
Total Cloud Cover
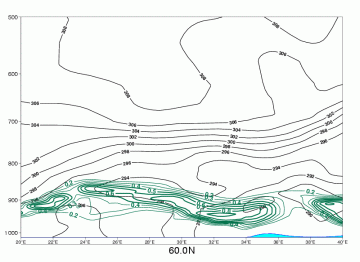
Advection Fog/St
|
|
09 November 2005/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; green: total cloud cover
|
Radiation Fog
|
|
04 October 2005/06.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; green: total cloud cover
|
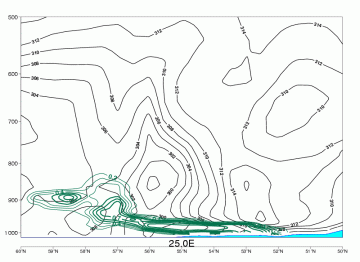
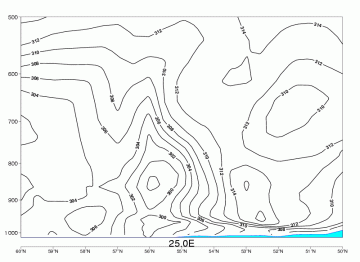
Isentropes
Advection Fog/St
|
|
09 November 2005/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes
|
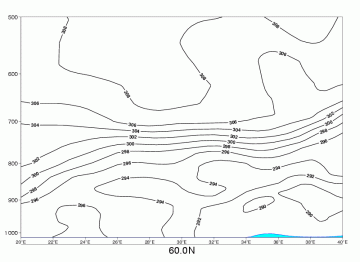
Radiation Fog
|
|
04 October 2005/06.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes
|
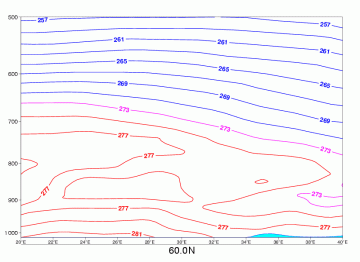
Temperature
Advection Fog/St
|
|
09 November 2005/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; red, magenta, blue: temperature
|
Radiation Fog
|
|
04 October 2005/06.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; red, magenta, blue: temperature
|