Typical Appearance In Vertical Cross Sections
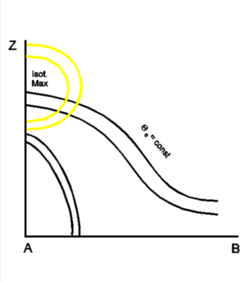
In the ideal case the isentropes of the equivalent potential temperature show two frontal gradient zones, an upper level front and a surface front. Both zones have Cold Front inclinations. While the upper level front is connected to the high leading cloud band, the surface front represents the low-level cloudiness to the rear of the frontal system. Whereas the zone of the surface front is pronounced, that of the upper level front is quite weak. Therefore, the upper level front is not characterized as a thermal boundary but rather as a moisture boundary (see Meteorological physical background).
The field of temperature advection often shows pronounced WA in front of and above the upper level frontal zone, which is connected with the upper level cloudiness. CA, typical for Cold Fronts, is situated below the surface front.
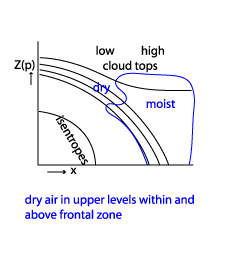
The most characteristic feature of the humidity distribution is a dry area at higher levels between the two frontal zones. High values of humidity can be found in front of the frontal zones.
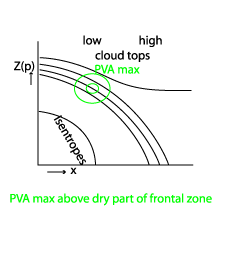
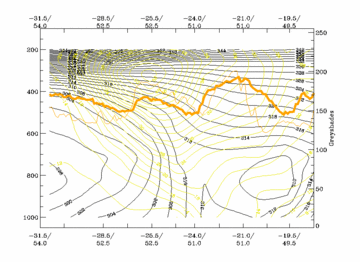
In the case of superimposed EC cloudiness, a distinct isotach and PVA maximum can be found above the surface front at approximately 300 hPa (see Front Intensification By Jet Crossing - Typical appearance in vertical cross section ).
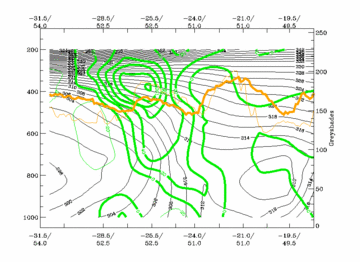
Looking at the distribution of humidity the satellite signals, IR and WV images show the highest pixel values in front of the upper level front and, if existing, within the EC - like cloud. To the rear of the upper level front the VIS signals are usually higher while IR and WV signals are much lower than those in front of the upper level front (see Cloud structure in satellite image).
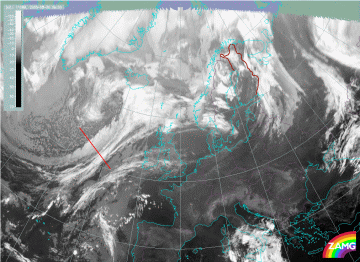
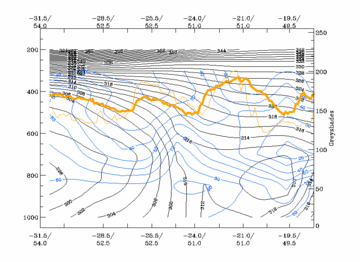
Compare the chapter Cloud structure in satellite image, where the cross section is indicated in the image. In contrast to the ideal case the surface Cold Front has a superadiabatic layer in the lower levels of the troposphere. The upper level Cold Front is well developed. The distribution of humidity shows the described insertion of drier air between the two frontal zones. The IR and WV images show the pronounced decrease of temperature from the low to the high cloud part.
|
30 August 2005/06.00 UTC - Meteosat 8 IR 10.8 image; position of vertical cross section indicated
|
|
30 August 2005/06.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (ThetaE), blue: relative humidity, orange
thin: IR pixel values, orange thick: WV pixel values
|
|
|
30 August 2005/06.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (ThetaE), green thick: vorticity advection
- PVA, green thin: vorticity advection - NVA, orange thin: IR pixel values, orange thick: WV pixel values
|
|
|
30 August 2005/06.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (ThetaE), yellow: isotachs, orange thin:
IR pixel values, orange thick: WV pixel values
|
|