3.5 - RGB images
RGB images can be used to extract information about vegetation cover. RGB techniques work by associating a colour to a particular channel.To extract maximum information from a single image each colour (Red, Green or Blue) should be associate to a different channel with distinct physical properties.
To extract information about vegetation cover, the RGB composite 1.6; 0.8; 0.6 μm, often referred as "Day natural colours" composite, can be used.
In this composite Red is associated to NIR 1.6 μm; Green to VIS 0.8 μm and Blue to VIS 0.6 μm. So as you can see in the image:
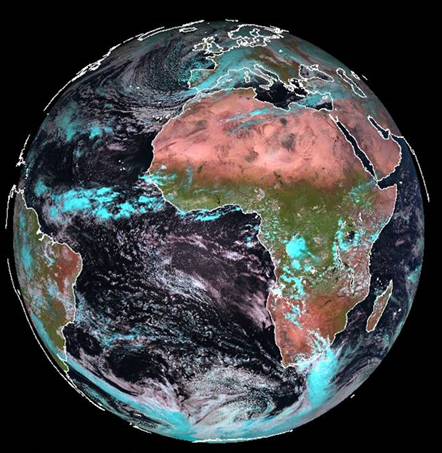
Figure 3.11: Meteosat-9 colour composite image of 1.6 μm, 0.8 μm and 0.6 μm
- Reddish/pink is dominant for bare soil and arid regions.
- Green is the dominant component for vegetation.
- Cyan is evident in ice clouds.
A complete description of how to apply RGB techniques in satellite images and forecasting, can be found in https://resources.eumetrain.org/IntGuide/