Chapter V: Vertical Cross Sections
Table of Contents
- Chapter V: Vertical Cross Sections
- Vertical Cross Sections
Vertical Cross Sections
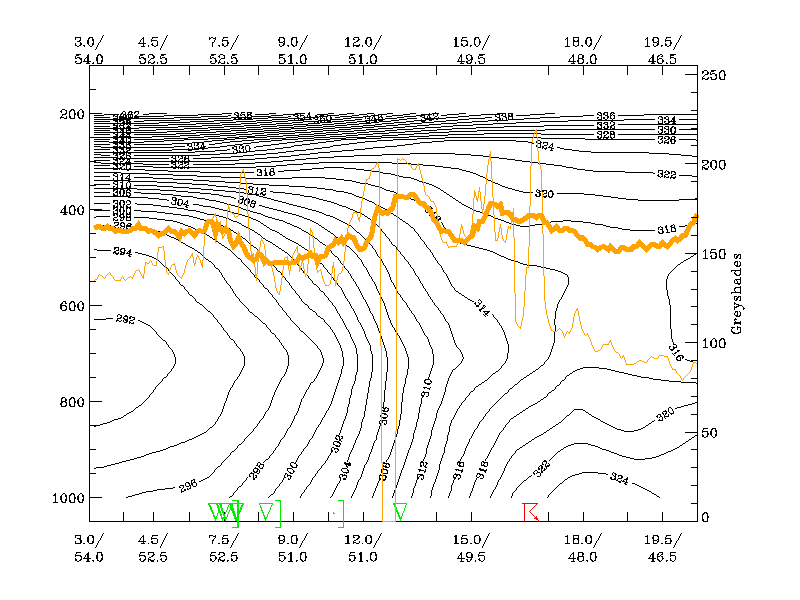
Both the frontal cloudiness and the MCS are well reflected in model fields. Isentropes show that in front of the frontal zone of high gradient, an unstable area with equivalent potential temperature decreasing from 324K at the surface to 316K in mid troposphere exists. Convergence is found along the frontal surface, but the most pronounced maximum is situated in the prefrontal area, near the surface, in the area where the MCS develop.
Figure 11: left: 13 May 2003/12.00 UTC - Meteosat IR image; position of vertical cross section indicated
13 May 2003/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (ThetaE), orange thin: IR pixel values, orange thick: WV pixel values
Figure 12: 13 May 2003/12.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (ThetaE), magenta thick: convergence, magenta thin: divergence, orange thin: IR pixel values, orange thick: WV pixel values