Cloud Structure In Satellite Images
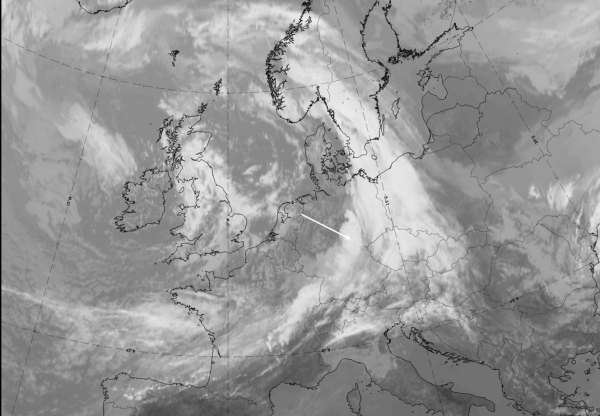
- The satellite image shows an area of increased cloud fraction (vertically and horizontally) within the frontal cloud band which also has a PVA maximum at 300 hPa superimposed on it (see Key parameters );
-
the increased cloud fraction can appear in two forms:
- Lumpy structure, which indicates embedded CBs
- Wave-like configuration, as a consequence of formation by cyclonic vorticity;
Appearance in the basic channels
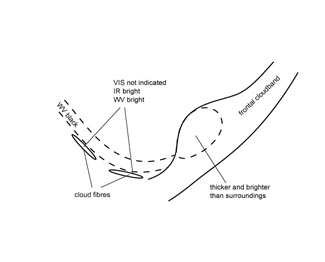
- VIS, IR and WV images show bright grey shades, indicating thick cloudiness (see Typical appearance in vertical cross section );
- this cloud feature is clearly brighter than the surrounding frontal cloudiness (see Key parameters );
- at the rear of the frontal cloud band, WV imagery indicates a jet axis pointing approximately perpendicular to the cloud band by a Black Stripe as well as Cloud Fibres which may also be seen in the IR image.
Appearance in the basic RGBs
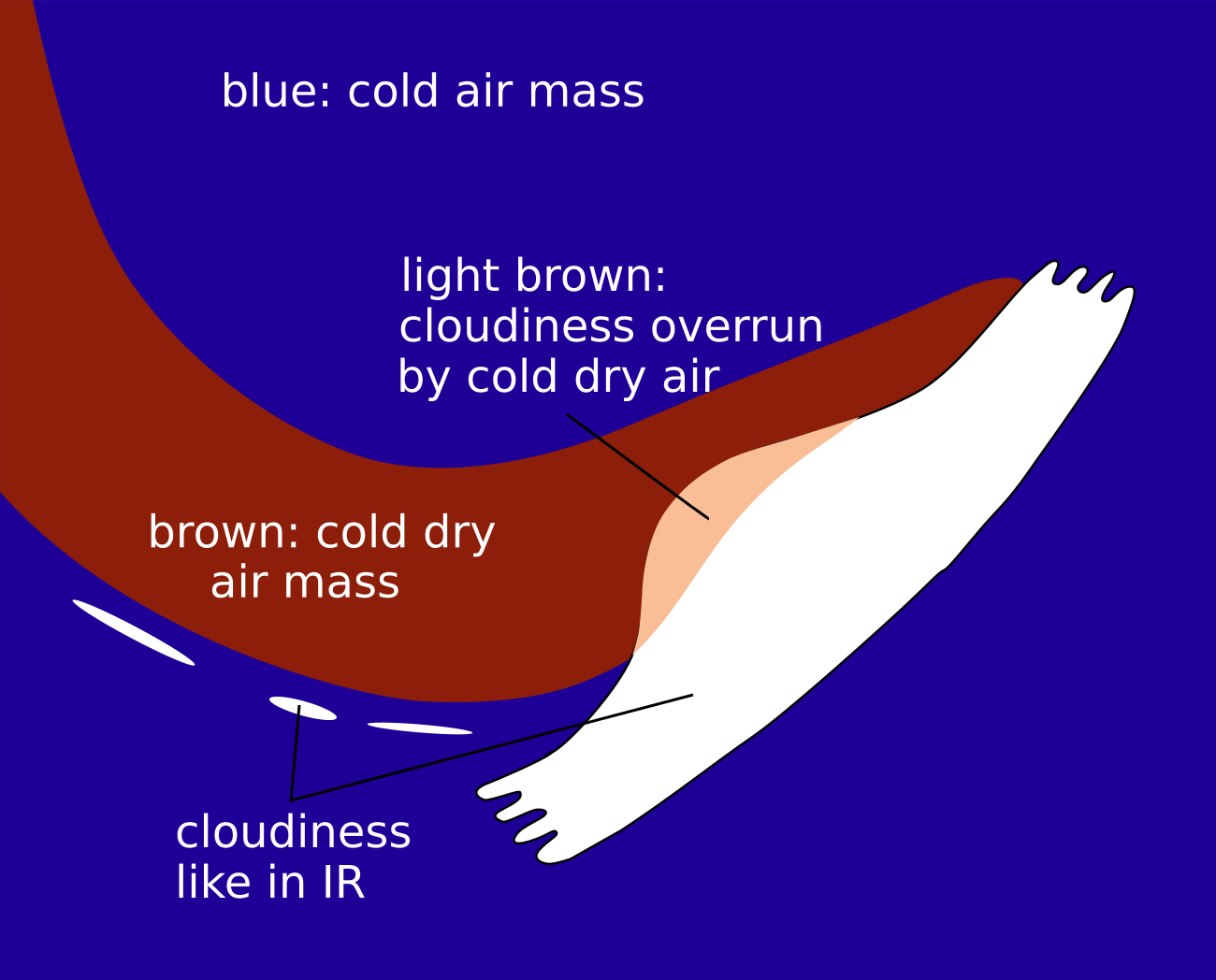
Airmass RGB
The increased cloud fraction associated with the “FI by Jet” area develops at the rear of the frontal cloud band. Behind the frontal cloud band and near the increased area of an “FI by Jet” there is a more or less broad, dark brown stripe which represents the dry cold air on the cyclonic side of the jet streak.
The increased cloud area of the “FI by Jet” looks very similar in the IR image. Sometimes there is a brownish shade at the rear of the “FI by Jet” area which shows that dry air is overrunning the frontal cloud band.
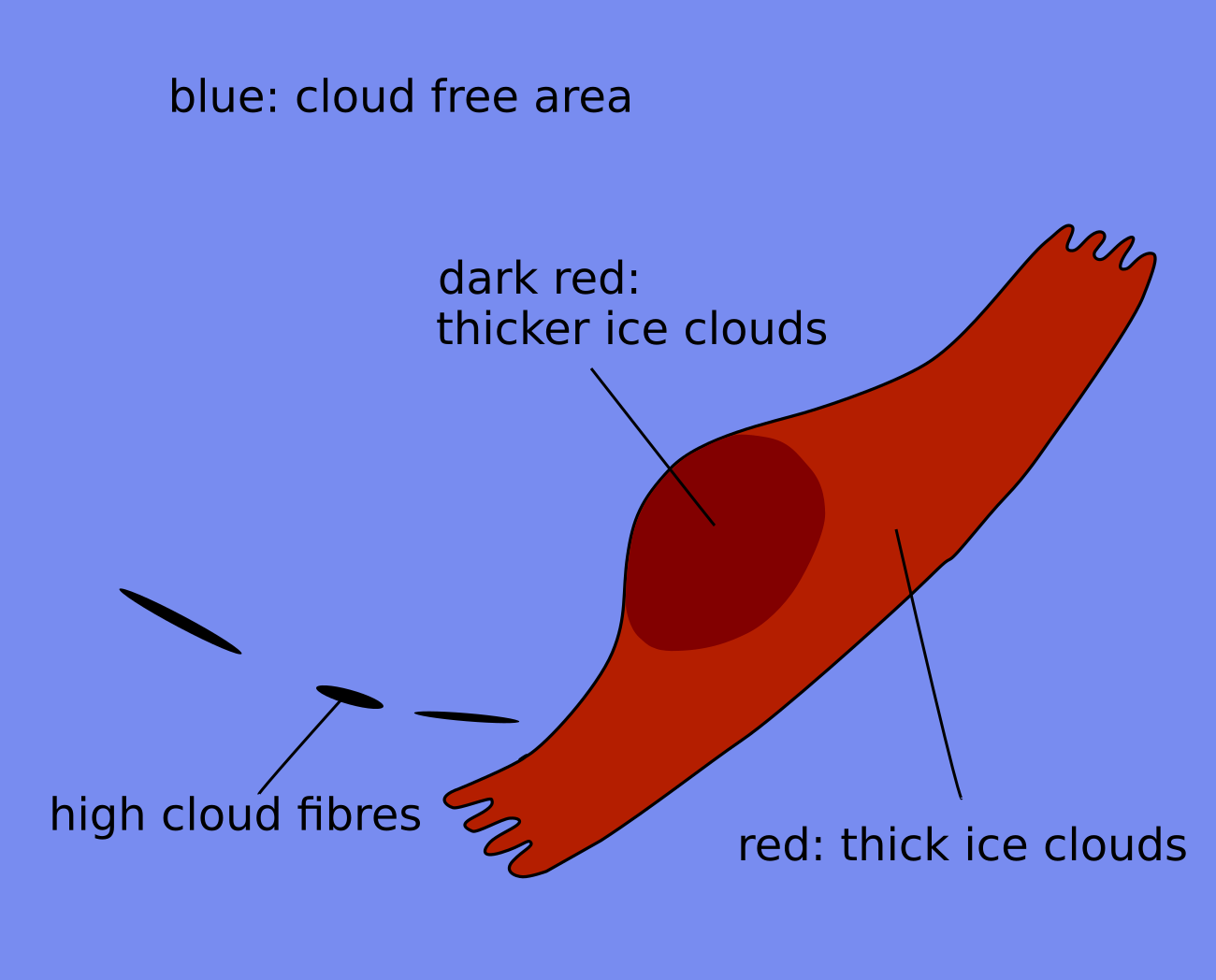
Dust RGB
At the rear of the “FI by Jet” cloud area the dust RGB shows blue colours where there are no other clouds. However, overall, there is the typical cold air cloudiness in this cold air outbreak which appears as ochre cells in the dust RGB. Some of them can also have a dark red appearance if they reach a greater vertical extension.
The cloud area of the "FI by Jet" sometimes shows up as dark red with some lumpy texture indicative of the thick convective cloud which is often higher and also thicker than in the surrounding Cold Front cloud band.
 |
 |
Legend: Schematics of basic RGBs.Left: Airmass RGB; right: dust RGB.
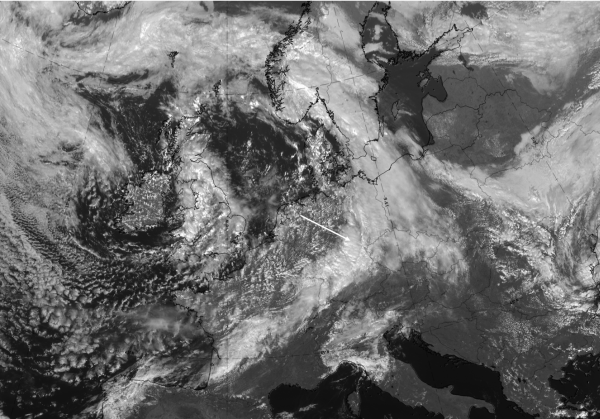
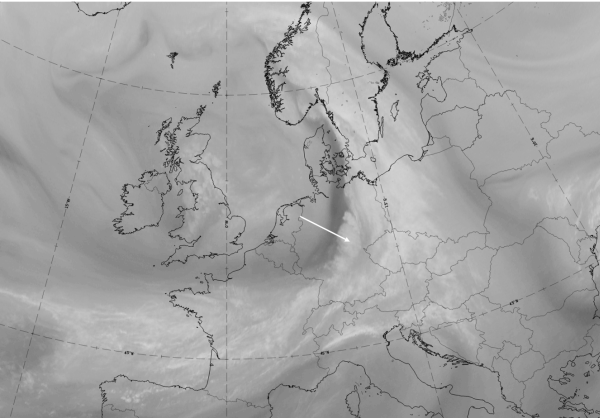
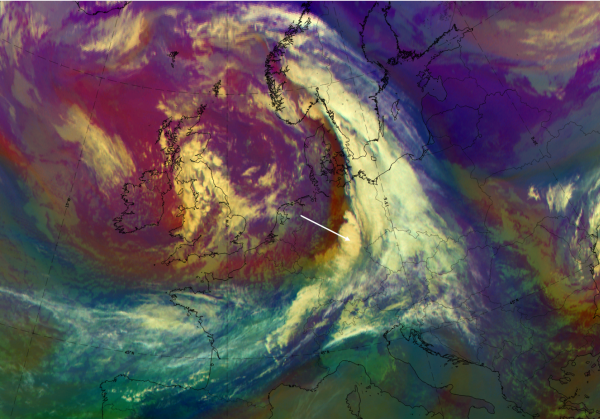
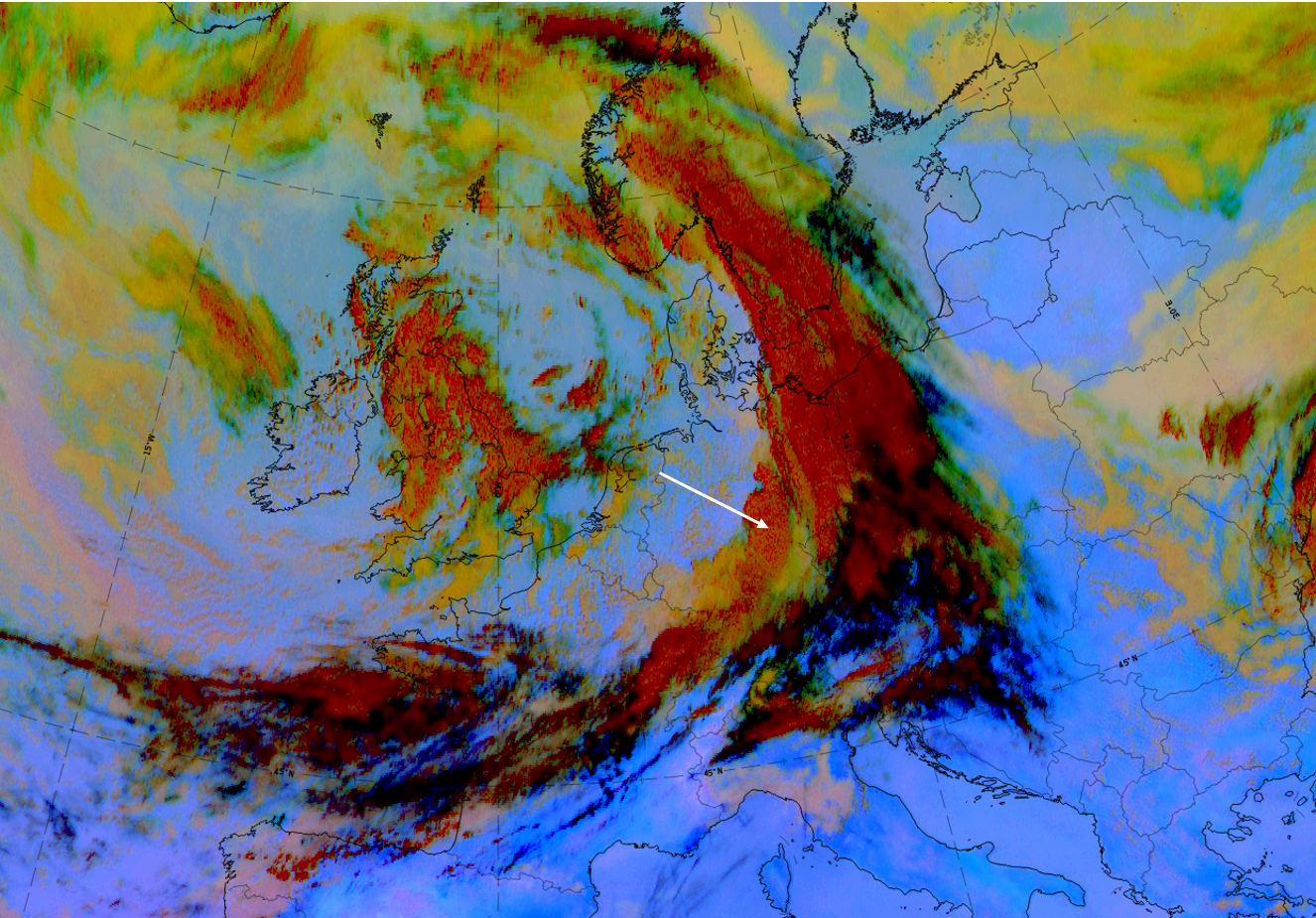
The case from 27 September 2019 at 12 UTC shows a large-scale frontal cloud band extending from France and across Germany to South Sweden and Norway. Additionally, an intensified cloud area can be observed over Germany.
|
|
|
|
27 September 2019, 12UTC: u.l.: IR, u.r.: HRV; m.l.: WV (6.2 μm), m.r.: Airmass RGB; l.l.: Dust RGB.
*Note: click on the Dust RGB image to access image gallery (navigate using arrows on keyboard)
| IR | White with convective cellular structure; jet fibres at the rear of the cloud band and the “FI by Jet” are not as distinct ion this case. They exist more to the SW from Brittany, eastward across France (more visible in the Dust RGB) |
| HRV | White with convective cellular structure. |
| WV | White with convective cellular structure; dark stripe at the rear representing sinking dry air. |
| Airmass RGB | Dark brown and/or blue behind the cloud band representing the cold and dry air; structures of "FI by Jet" similar to IR but with a brownish shadow indicating overrunning dry air. |
| Dust RGB | Dark red colours in the “FI by Jet” indicating thick ice cloud above the ochre colours for mid-level cloud; black cloud fibres indicate high translucent cloud at the jet axis; in this case something can be seen over France but it is not as distinct as it often is in other cases. |