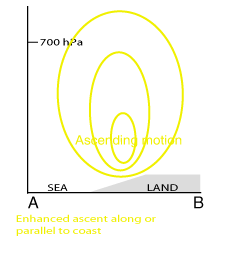
Typical Appearance In Vertical Cross Sections
The extent of circulation induced by Coastal Convergence depends on the general stability of the lower troposphere. In stable conditions the circulation is restricted to the lowest kilometre of the atmosphere, whereas in unstable conditions Coastal Convergence can be conducive to deep convection.
- Divergence:
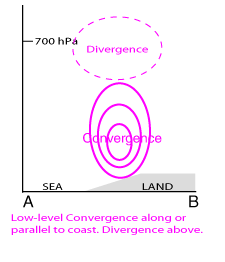
Low-level Convergence along or parallel to coast, typically maximum below 2 km altitude. Divergence above. - Vertical motion:
Enhanced ascent along or parallel to coast.
|
|
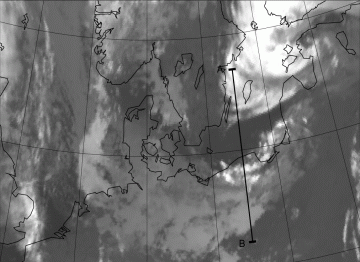
31 July 2007/00.00 UTC - Meteosat 9 10.8 image; position of vertical cross section indicated
|
Divergence
|
|
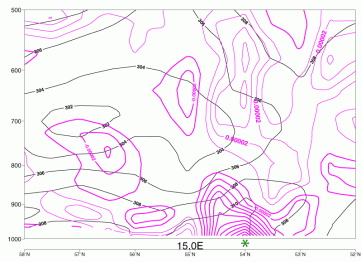
31 July 2007/00.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (ThetaE), magenta thick: convergence, magenta thin: divergence;
Location of Polish coastline is shown with a green star.
|
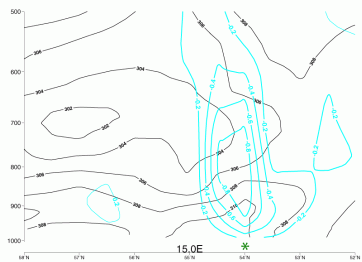
Vertical motion
|
|
31 July 2007/00.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (ThetaE), cyan thick: vertical motion (omega) - upward motion,
cyan thin: vertical motion (omega) - downward motion; Location of Polish coastline is shown with a green star.
|