Typical Appearance In Vertical Cross Sections
- ThetaW:
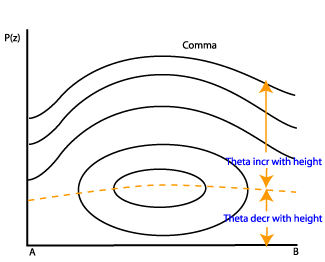
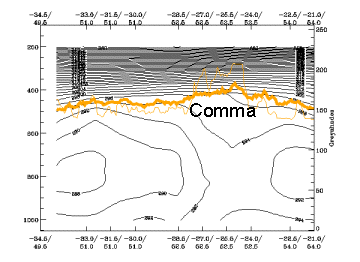
One of the most characteristic properties of Commas is the instability in lower and middle levels. The unstable air mass is indicated by the distribution of the isentropes up to 800 - 700 hPa. In most cases no frontal character can be seen in the lower troposphere, but in upper levels (above 500 or 600 hPa) sometimes one can see a downward inclination of the isentropes leading to a higher gradient. The peak belonging to the Comma feature under consideration is the one in the right half of the cross section (52.5N/24W). The more western peaks belong to convective areas in the centre of the Comma spiral. - Relative Vorticity:
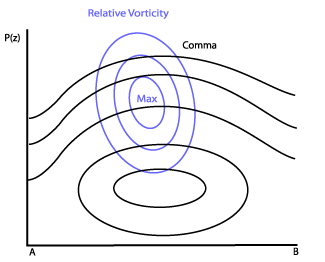
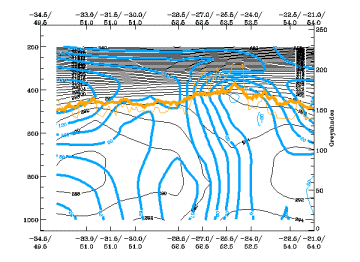
Commas exist in areas of positive relative vorticity throughout the whole vertical cross section. The maximum lies to the rear at about 400 hPa (never below 500 hPa and not higher than 300 hPa). - Vorticity Advection (PVA/NVA):
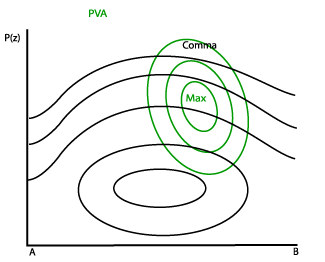
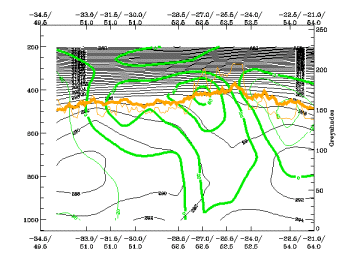
Vertical cross sections show PVA above the cloudy area with its maximum in the upper troposphere, in advance of the corresponding vorticity maximum. There can be both PVA and NVA behind and in front of the Comma. - Omega:
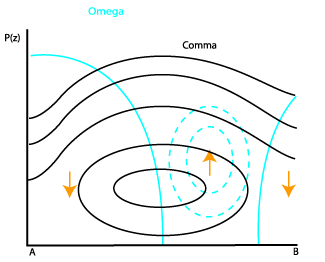
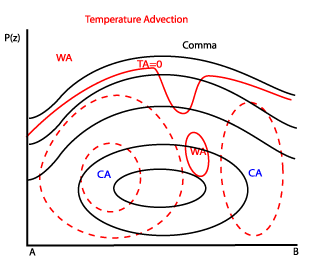
Commas are often associated with upward motion throughout the whole atmosphere. - Temperature Advection:
The profile of temperature advection usually shows cold advection in the lower levels trough out the whole area of the Comma. In middle and upper-levels some warm advection can be found over the cloudy area, and cold advection behind the Comma. - Divergence:
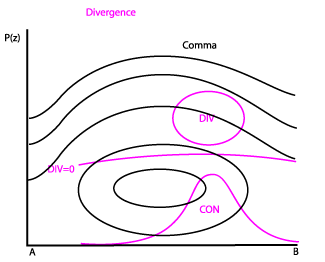
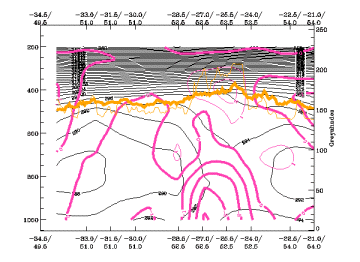
The vertical distribution of divergence shows convergence in lower levels often decreasing with height; that can result in divergence in upper levels. This is consistent with upwards motion (see above). Convergence is generally found near the cloudy area but may sometimes be present in the surrounding areas. Convergence is occurring in this case in a thick layer from the surface up to 700 hPa.
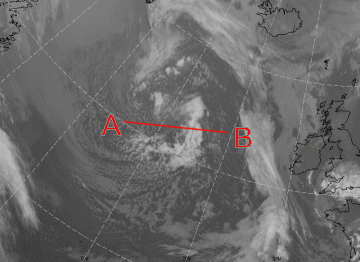
As shown below the appearance of a Comma in a vertical cross section is best described by a cross section taken south of the Comma head.
|
25 April 2005/06.00 UTC - Meteosat 8 IR 10.8 image; position of vertical cross section indicated
|
|
ThetaW
|
|
25 April 2005/06.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (ThetaE), orange thin: IR pixel values, orange thick: WV pixel
values
|
Relative Vorticity
|
|
25 April 2005/06.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (ThetaE), blue: relative vorticity, orange thin: IR pixel
values, orange thick: WV pixel values
|
Vorticity Advection (PVA/NVA)
|
|
25 April 2005/06.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (ThetaE), green thick: vorticity advection - PVA, green thin:
vorticity advection - NVA, orange thin: IR pixel values, orange thick: WV pixel values
|
Vertical Motion (Omega)
|
|
25 April 2005/06.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (ThetaE), cyan thick: vertical motion (omega) - upward motion,
cyan thin: vertical motion (omega) - downward motion, orange thin: IR pixel values, orange thick: WV pixel values
|
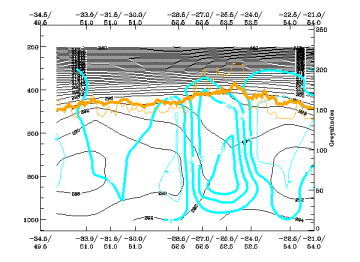
Temperature Advection
|
|
25 April 2005/06.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (ThetaE), red thick: temperature advection - WA, red thin:
temperature advection - CA, orange thin: IR pixel values, orange thick: WV pixel values
|
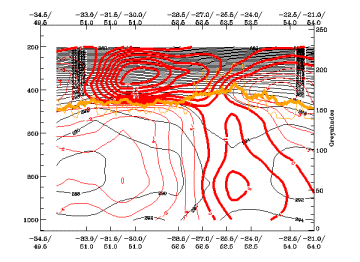
Divergence
|
|
25 April 2005/06.00 UTC - Vertical cross section; black: isentropes (ThetaE), magenta thin: divergence, magenta thick: convergence,
orange thin: IR pixel values, orange thick: WV pixel values
|