Summary of the validation
A complete account of the validation methodology and results is found in "Validation Report for PGE13 SPhR v1.2" (Martinez, Romero and Li, 2012c). This section summarizes it. The satellite-retrieved temperature and humidity profiles and convective environmental parameters (water vapor content and instabilities) were verified for the full METEOSAT disk for the year 2009. The outputs were calculated with the background ECMWF fields from a previous run 12 hour forecast and verified against ECMWF analysis: temperature and moisture profiles of the 91 hybrid levels and the environmental parameters calculated from them. The results are shown in Figs. 1 and 2 and in Table 1.
 Figure 1: RMSE of the satellite-retrieved humidity volume mixing ratio profiles (q, ppmv) from January to December 2009 for sea pixels (left) and land pixels (right). The black, red and green curves correspond to the background NWP, first guess and first iteration retrieval, respectively.
Figure 1: RMSE of the satellite-retrieved humidity volume mixing ratio profiles (q, ppmv) from January to December 2009 for sea pixels (left) and land pixels (right). The black, red and green curves correspond to the background NWP, first guess and first iteration retrieval, respectively.
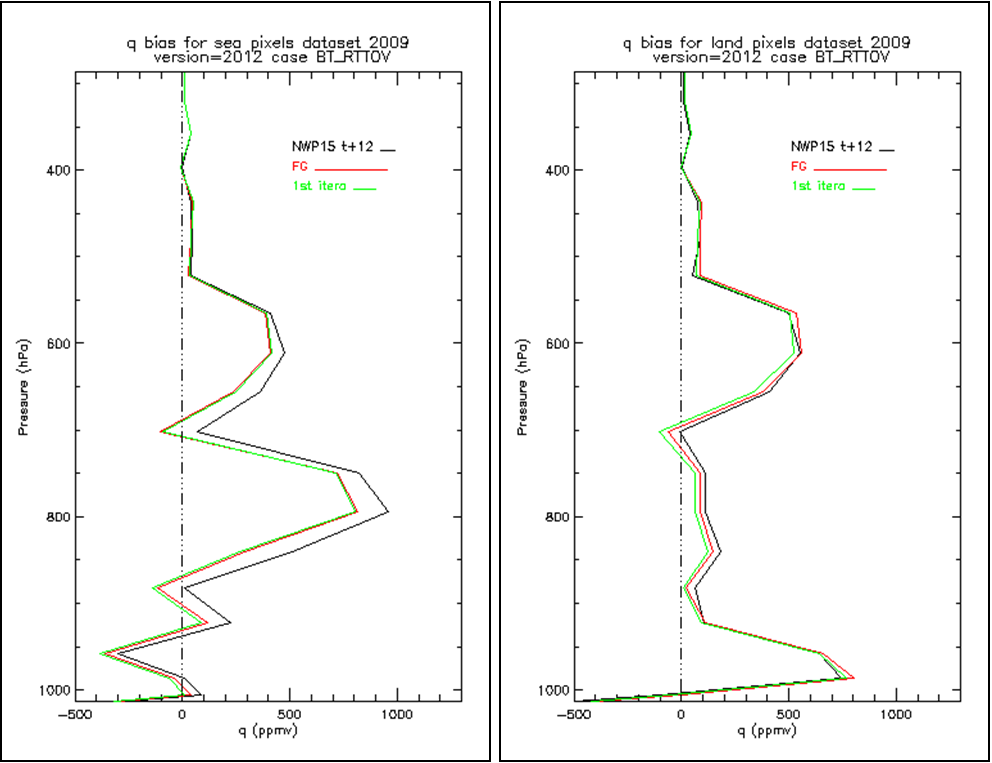 Figure 2: Bias of the satellite-retrieved humidity volume mixing ratio profiles (q, ppmv) from January to December 2009 for sea pixels (left) and land pixels (right). The black, red and green curves correspond to the background NWP, first guess and first iteration retrieval, respectively.
Figure 2: Bias of the satellite-retrieved humidity volume mixing ratio profiles (q, ppmv) from January to December 2009 for sea pixels (left) and land pixels (right). The black, red and green curves correspond to the background NWP, first guess and first iteration retrieval, respectively.
Table 1 summarizes the verification.
| Against ECMWF Analysis Full disk validation | Low Layer Precipitable Water (BL)/[kg/m2] | Medium Layer Precipitable Water (ML)/[kg/m2] | High Layer Precipitable Water (HL)/[kg/m2] | Total Precipitable Water (HL)/[kg/m2] | Lifted Index (LI)/[K] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Over Sea | 0.91 | 1.64 | 0.15 | 1.84 | 1.00 |
| Over Land | 0.79 | 1.43 | 0.16 | 1.64 | 1.09 |
Table 1: Summary of verification of layer water vapor contents, TPW and the Lifted Index.
The final conclusion of the developers (Martinez, Romero and Li, 2012c) is that the PGE13 SPhR can provide useful spatial information, but SEVIRI has a limited capacity to improve on vertical information. The PGE13 SPhR can make only minor improvements to the NWP information of mid-troposphere humidity profiles.