Authors
Meteorological and Hydrological Service of Croatia - DHMZ
Dunja Placko-Vrsnak
Natasa Strelec Mahovic
Dunja Drvar
Introduction
The case study will deal with the severe convective development within a cold front over Turkey. On the 25th of May convective development occurred ahead of the front in the warm sector, induced by orography. During the 26th of May a distinct line of prefrontal convergence can be followed, as well as the convection over Eastern Turkey, far ahead of the front. The case is affirmed by thunderstorm and hail reports (data is not available here). The whole course of development and the onset of the convective events is discussed in detail with help of the satellite and radar images as well as the relevant NWP parameters.

|
|
Meteosat 8 HRV : 26 May 2006, 12 UTC Click to enlarge. |
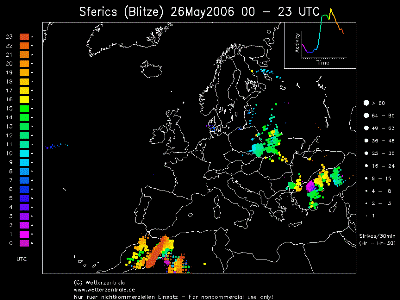
Lightning reports during 26 May 2006 Click to enlarge. |
The left image shows convective clouds over Western and Central Turkey - the biggest cells correspond to convective activity within the cold front. The line of smaller cells belongs to prefrontal convergence. Convective clouds over Eastern Turkey are connected to the upper level low. Reports of thunderstorms can be seen in the right image - lightning occurred during the whole day on the 26th of May. The size of the dots indicates the frequency of lighting during 30 minutes period (the bigger the dot - more frequent the strikes during the time period).

|
|
Meteosat 8 RGB 01-03-09i - 26 May 2006 : 10 UTC Convective cells within cold front over Central Turkey. |
Combinations and differences of satellite channels enable a deeper insight into the synoptic situation, structure of cloudiness and development over some area, but also help us to see in more detail things that are interesting and unusual for a particular location.
In the image above a red spot in mid-Turkey can be noticed. In this RGB combination yellow colour represents low clouds or fog, bluish colour displays high thin cold clouds and pinkish colour is connected to thick convective clouds. Red colour in the Meteosat 8 RGB 01-03-09i is usually used to detect snow cover over mountains. However the red spot in this image represents salt lake Tuz located at an altitude of about 900 meter. The lake is very shallow and during the hot part of the year it evaporates. The reflectivity of the salt crystals is similar to the reflectivity of the ice crystals, hence in this RGB it is presented by the dark red colour.
The aim of this case study is to:
- Show the onset of convective event using various Meteosat 8 channels and artificially coloured combinations
- Show the onset of convective event using radar images (reflectivity)
- Study satellite imagery in combination with NWP fields
- Investigate the dynamical background of the processes by considering the basic and derived numerical model parameters
This case study will show that the analysed convective episodes have similarities and differences. To be able to follow the case study from the beginning it is preferable to study the chapter dealing with convective weather features from the “Manual of Synoptic Satellite Meteorology”.
EUMeTrain, 2007