Authors
DWDWilfried Jacobs
Introduction
This case study is about an unusual development of a super cell over the North Sea and its moving to Northern Germany in relation to a warm front wave. The frontal zone extended from South Scandinavia to Poland. An important fact is that Northern Germany was under the warm site of the frontal zone. A short wave trough moved quickly from the North Sea to the Chech Republic yielding an intense dynamical forcing. Upward motion in connetion with a warm front wave caused a super cell over the North Sea that moved later on to Southeast. Till noon the whole complex weakened before intensifying again during the afternoon. However, we will scope only to the time period 00 to 09 UTC (NWP-fields to 12 UTC)

|

|
Precipitation amounts of up to 20 mm/hr were reported. In the vicinity of the super cell gusts between Beaufort 9 and 10 were observed. Damages due to hail, storm and lightning occured:
|
|
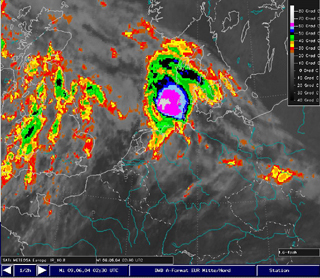
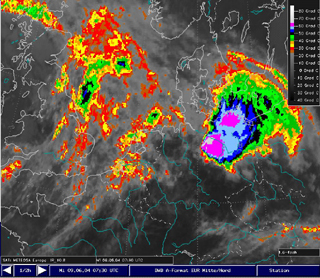
| Meteosat 8 IR10.8: 09th June 2004, 02:30 UTC The super cell achieved the highest intensity. Cloud top temperature of less than -65°C (equivalent to the temperature of the tropopause) were detected. | Meteosat 8 IR10.8: 09th June 2004, 07:30UTC. The super cell after the „severe right moving“ and just after the highest intensity of the right part. Again, cloud top temperatures below 65°C, i.e. cloud tops extending above the tropopause. |
The aim of this case study is to:
- Follow the development of the super cell (different channels, colour tables, fine structures)
- Investigation of the dynamical background by considering the basic observations / measurements and numerical parameters
- Very warm and humid air, potential unstable
- Frontal zone near-by and upward motion
- Increasing wind speed with height and strong vertical wind shear, especially in the lowest levels
- Satellite image: Fast vertical and spatial growing of a cloud cluster
- More circular form, most intense convection near the centre of the cloud cluster (overshootings, lightning and radar)
- V-Notch: Stretched IR-cloud top-temperatures and composits of differences between MSG-channels
- Overshootings: Comparision of WV and IR-images
- Confluence near the surface, sometimes cyclonic circulation
- After passing of the super cell strong positive surface pressure tendencies.
- Surface pressure and tendency
- Pseudopotential temperatures
- 10m-wind and gusts
- Geopotential 300 hPa
- Voriticity advection 300 hPa
- Vertical motion 500 hPa in combination with KO-index
- Temperature advection in 500 hPa